Rigging in 3D Animation
Rigging is a vital stage in 3D animation that allows static 3D models to move realistically. It involves creating a digital skeleton for characters or objects, defining joints, bones, and control systems so animators can manipulate them efficiently. Without rigging, models remain static and cannot perform the complex movements required for animation, games, or films.
What is Rigging in 3D Animation?
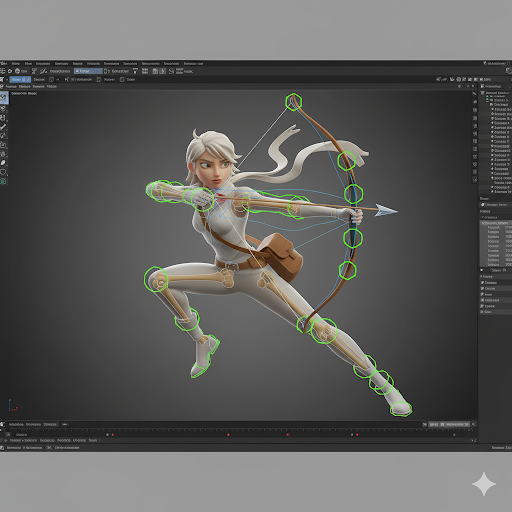
Rigging is the process of adding a skeleton and control mechanisms to a 3D model. This skeleton acts like the bones of a real creature, with joints, constraints, and controllers that guide motion. Rigging ensures that when animators move a part of the model (like an arm or a leg), the mesh deforms naturally, maintaining realism and expressive flexibility.
Rigging is also crucial for mechanical objects or props, allowing parts to move according to designed rules, such as doors, robots, or vehicles.
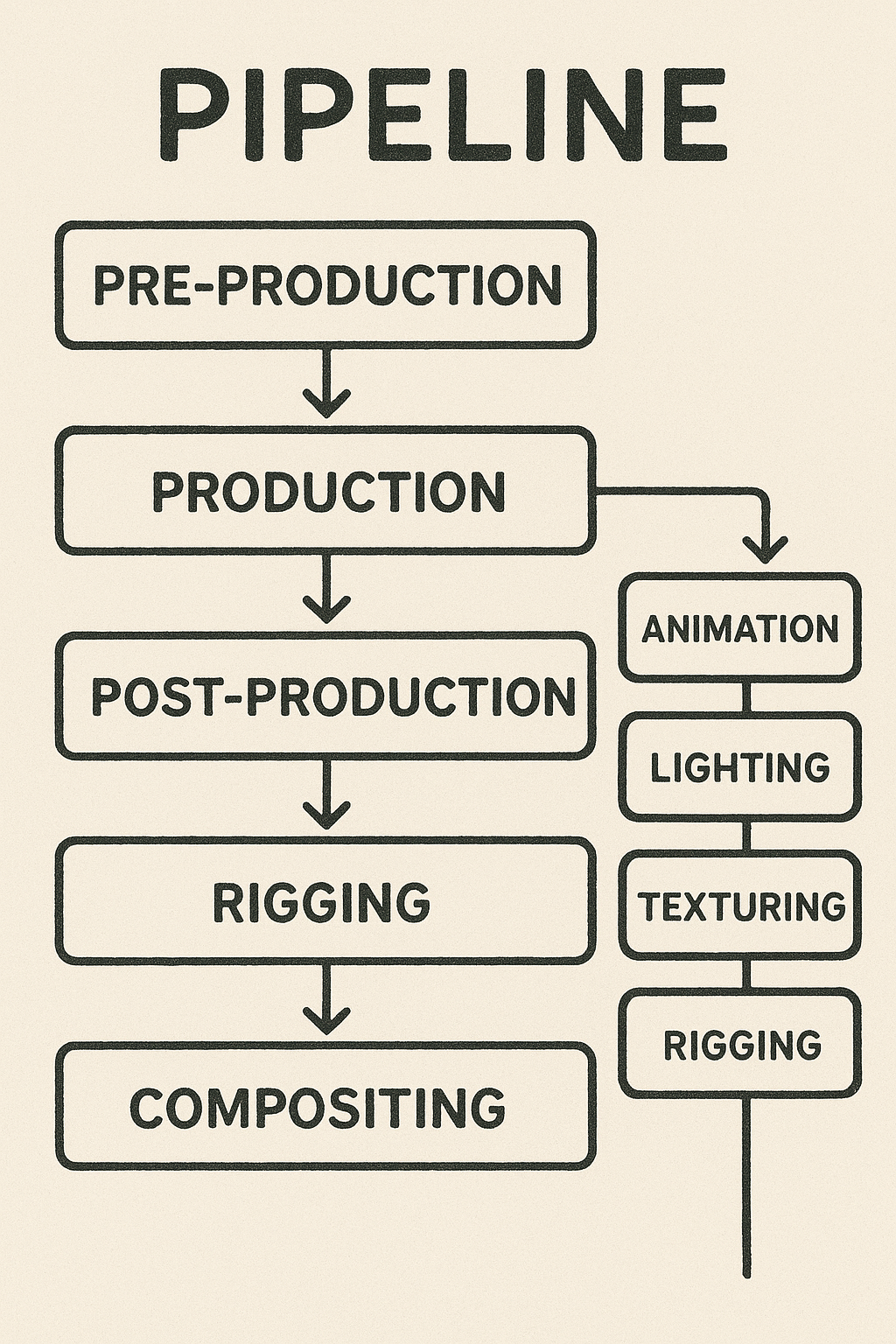
Key Steps in Rigging
- Skeleton Creation
Place bones and joints inside the 3D model to match its structure.Define hierarchical relationships to ensure proper movement. - Skinning & Weight Painting
Bind the 3D mesh to the skeleton.Assign weights to control how much influence each bone has over surrounding vertices. - Adding Controls & Constraints
Set up controllers for animators to manipulate complex motions easily.Constraints limit unrealistic movements, ensuring natural animation - Testing & Refinement
Move joints through different poses to check mesh deformation and control responsiveness.Adjust weights and controllers to eliminate distortions. - Facial & Advanced Rigging (Optional)
For characters, create facial rigs with bones or blend shapes for expressions.Enables lip-sync, emotions, and subtle movements.
Why Rigging Matters
Rigging is the bridge between modeling and animation. A well-rigged model allows animators to focus on creativity and storytelling without worrying about unnatural deformations or technical issues. It saves time, improves efficiency, and ensures the final animation looks polished and believable.
Pros of Rigging in 3D Animation
- Enables Realistic Movement – Characters and objects can move naturally.
- Efficient Animation Workflow – Provides animators with control handles to speed up animation
- Reusable Assets – A rig can be reused for multiple characters or models.
- Flexibility – Allows both subtle and complex motions, from expressions to full-body actions.
- Supports Advanced Animation – Essential for game characters, cinematic sequences, and simulations.
- Error Prevention – Proper rigging avoids mesh distortions and motion inconsistencies during animation.
Conclusion
Rigging serves as the backbone of character animation, transforming static 3D models into dynamic, lifelike entities capable of expressive motion. It bridges the gap between modeling and animation, allowing animators precise control over movement and articulation. Mastering rigging not only enhances the realism and fluidity of animated sequences but also streamlines the workflow in production pipelines. As animation technology evolves, rigging continues to be an essential skill for creating compelling, believable characters in games, films, and virtual experiences.
Thumbnail
A thumbnail could feature a 3D character split into two halves: one half showing the raw mesh, and the other half showing the rigged skeleton with joints and control handles. Overlay subtle motion arrows to indicate flexibility, and include a stylus or animation software interface in the background. This visual instantly communicates “rigging transforms a static model into an animatable character.